Blog
Ketamine therapy

In the landscape of mental health treatment, a new player has emerged, capturing the curiosity of researchers, practitioners, and patients alike: ketamine therapy. Once primarily known as an anesthetic and, in some circles, a party drug, ketamine is now being explored for its potential to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder. As the stigma surrounding its use begins to wane, the conversation shifts from skepticism to investigation, opening doors to innovative approaches in psychiatry. In this article, we delve into the science, the burgeoning practice, and the experiences that surround ketamine therapy, seeking to uncover how this unconventional treatment is reshaping the narrative around mental health care.
Exploring the Mechanisms of Ketamine Therapy for Mental Health
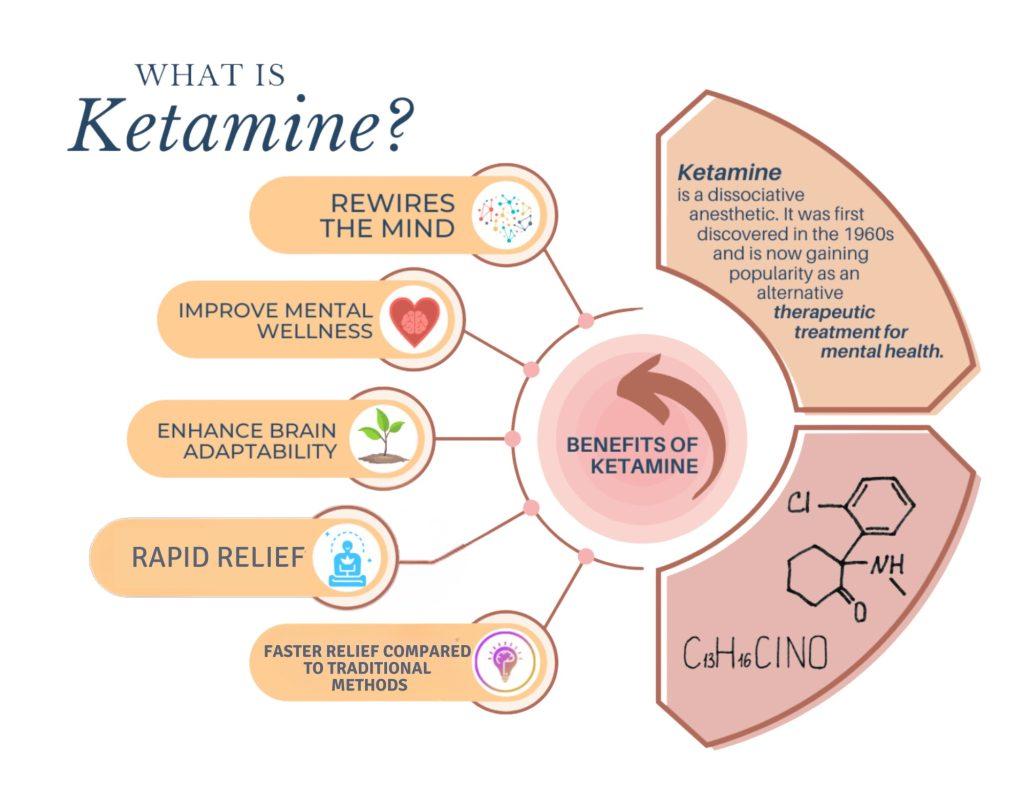
Ketamine therapy has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the treatment of various mental health conditions, marking a significant departure from traditional pharmacological therapies. This unique treatment is based on the substance’s ability to simultaneously influence NMDA receptors and enhance glutamate transmission, which fosters increased synaptic connectivity within the brain. Research suggests that these actions can lead to a rapid alleviation of symptoms associated with depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), often providing relief where conventional medications have failed.
Through its neuroplastic effects, ketamine promotes brain resilience and adaptive changes, leading to significant improvements in mood and cognitive function. The therapy can be administered in various forms, including intravenous, intranasal, or even oral; however, the method and dosage often depend on individual patient needs. Here’s a quick overview of the different methods of administration:
| Method | Administration | Onset Time |
|---|---|---|
| Intravenous | Directly into the bloodstream | Rapid, within minutes |
| Intranasal | Sprayed into the nose | Moderate, around 15 minutes |
| Oral | Swallowed as a pill | Slower, approximately 30-90 minutes |
Clinical Applications: From Depression to PTSD in Ketamine Treatment
Innovative approaches in ketamine therapy have brought attention to its clinical versatility, paving the way for treatment across a spectrum of mental health conditions. One primary application is in the management of depression, especially treatment-resistant depression—a condition where traditional medications fail to provide relief. Studies reveal that ketamine can produce rapid antidepressant effects, often within hours, which contrasts sharply with the weeks required for conventional antidepressants. This fast-acting quality not only underlines its potential in crisis scenarios but also brings hope to patients who have felt trapped in cycles of despair. Furthermore, ketamine’s impact on neuroplasticity appears to facilitate long-term improvements in mood and cognition, reshaping the conversation around effective therapeutic options.
In addition to depression, ketamine therapy has shown promise in the treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). The experience of trauma can linger, leading to debilitating symptoms that disrupt daily functioning and quality of life. Ketamine’s ability to disrupt negative thought patterns and allow for emotional processing offers new pathways for recovery in PTSD patients. Many treatment protocols combine ketamine therapy with psychotherapy, enhancing the benefits of both approaches. Below is a summary of the conditions where ketamine therapy has made significant strides:
| Condition | Effects of Ketamine Therapy |
|---|---|
| Depression | Rapid relief from depressive symptoms |
| PTSD | Enhanced emotional processing and reduction of intrusive memories |
| Anxiety Disorders | Reduction of symptoms in generalized and social anxiety |
| Chronic Pain Syndromes | Potential alleviation of pain perception |
Navigating the Ketamine Journey: What to Expect During Therapy Sessions
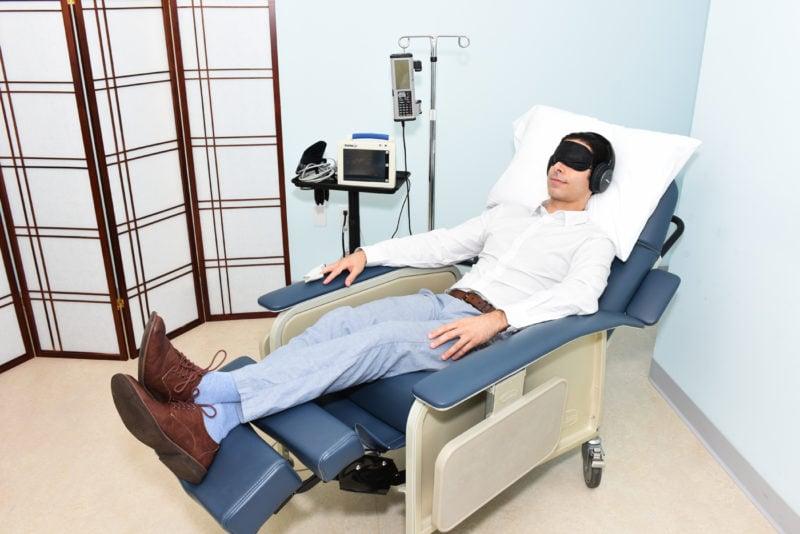
Embarking on a journey through ketamine therapy can be both exciting and daunting. As you step into the therapy room, you might find yourself in a calming environment, often adorned with soothing colors and ambient music to set the right mood. During your sessions, you will likely notice a few key elements that are central to the experience. Expect to be monitored closely by a trained professional throughout the process, as they carefully assess your emotional and physical responses. The typical session might include:
- IV or Intranasal Administration: Depending on your treatment plan, ketamine may be delivered through an intravenous line or nasal spray.
- Relaxation Techniques: Therapists often guide patients through breathing exercises or mindfulness practices to enhance the experience.
- Integration Support: After the infusion, you’ll have time to process feelings and thoughts that arise during therapy.
Many individuals report feeling a sense of detachment, which can be a pivotal aspect of the therapeutic experience. This altered state can lead to profound insights and emotional breakthroughs. It’s also common to encounter a range of sensations, from warmth and euphoria to deep introspection. Additionally, the therapy sessions are typically structured to promote safety and comfort, with a focus on the following:
| Session Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-Session Consultation | Discuss goals, medical history, and expectations with your therapist. |
| Monitoring | Continuous observation of vital signs and emotional wellbeing. |
| Post-Session Reflection | Time to share experiences and feelings in a guided discussion. |
Safety and Efficacy: Understanding the Risks and Best Practices in Ketamine Use
As the popularity of ketamine therapy grows, it is essential to weigh its potential benefits against the possible risks involved. The efficacy of ketamine in treating conditions such as depression and PTSD can be remarkable; however, the following considerations are crucial in ensuring safety:
- Proper Screening: Individuals should undergo thorough psychological and physical assessments prior to treatment.
- Credentialed Professionals: Only licensed practitioners should administer ketamine in a controlled environment.
- Dosage Monitoring: Close monitoring of dosage and patient response is critical to minimize adverse effects.
- Follow-Up Care: Continuous support and follow-up appointments are important for long-term outcomes.
Moreover, understanding the context in which ketamine is used can further enhance safety and efficacy. Studies have emphasized the importance of combining ketamine treatment with psychotherapy to achieve optimal results. In scenarios where ketamine is used, the following best practices should be observed:
| Best Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Integrative Approach | Combining ketamine treatment with therapeutic modalities for enhanced results. |
| Patient Education | Informing patients about potential effects and ensuring they understand the process. |
| Environmental Safety | Providing a calm, safe environment during administration to reduce anxiety. |
To Wrap It Up
As the landscape of mental health treatment continues to evolve, ketamine therapy stands out as a beacon of hope for many seeking relief from persistent psychological distress. Its unique properties and rapid effects have opened new doors in the understanding of mood disorders, offering a glimmer of optimism for those who have long struggled with traditional methods. However, as we navigate the complexities of this emerging therapy, it is essential to approach it with informed caution and an open mind. Continued research and patient-centered practices will be crucial in shaping its role within our broader healthcare system. As we turn the page on conventional paradigms and embrace innovative approaches, the potential of ketamine therapy invites us all to contemplate a future where healing knows no bounds.